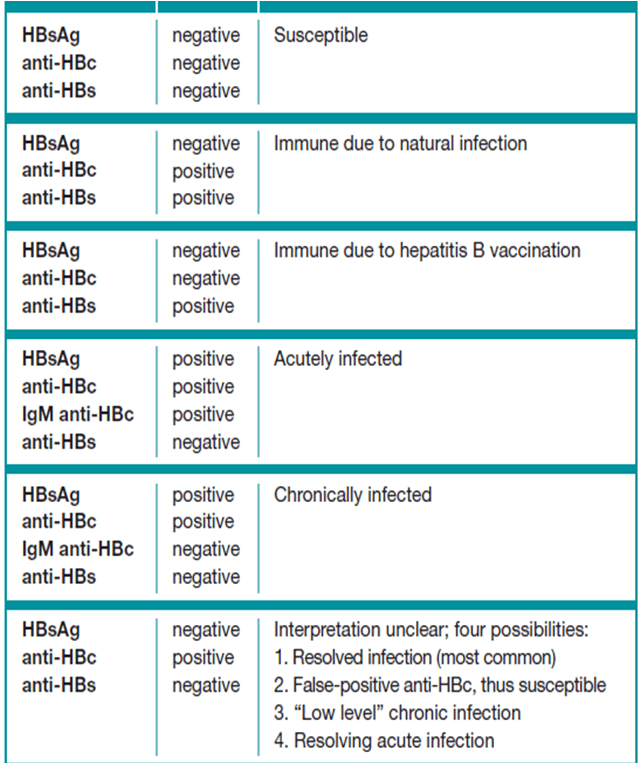
Total anti-HBc Positive IgM anti-HBc Negative 1 Anti-HBs Negative: Understanding Hepatitis B Immunity
A Comprehensive Guide to Interpretation
Introduction
Hepatitis B is a viral infection that affects the liver. Testing for hepatitis B involves evaluating various antibodies to determine immunity or previous exposure. One common test result combination is Total anti-HBc Positive IgM anti-HBc Negative 1 Anti-HBs Negative. Understanding the interpretation of these results is crucial for assessing hepatitis B status and making informed decisions.
Interpretation of Results
Total anti-HBc Positive: This indicates the presence of antibodies against the hepatitis B core antigen (HBcAg), which suggests a past or current infection with hepatitis B.
IgM anti-HBc Negative: This means that there are no detectable IgM antibodies against HBcAg, which usually indicates that the infection is not active or has resolved.
Anti-HBs Negative: The absence of antibodies against hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) suggests that the individual is not currently immune to hepatitis B.
Clinical Significance
The test result combination of Total anti-HBc Positive, IgM anti-HBc Negative, and Anti-HBs Negative indicates that:
- The individual has been infected with hepatitis B in the past.
- The infection has resolved or is no longer active.
- The individual is not currently immune to hepatitis B.
- Get Vaccinated: Individuals with Total anti-HBc Positive and Anti-HBs Negative results should receive the hepatitis B vaccine to establish immunity.
- Monitor for Reactivation: Individuals with a history of hepatitis B infection should be monitored for potential reactivation of the virus, especially in immunosuppressed individuals.
- Retesting: Repeat testing may be recommended after a period of time to assess immune status and determine the need for further vaccination or monitoring.
Possible Explanations
Vaccination: If an individual has received the hepatitis B vaccine, they may produce antibodies against HBcAg (Total anti-HBc Positive) without developing antibodies against HBsAg (Anti-HBs Negative).
Past Infection: Individuals who have recovered from a hepatitis B infection may have Total anti-HBc Positive and Anti-HBs Negative results, indicating a past infection but no current immunity.
Recommendations
Based on these results, the following recommendations may be made:
Conclusion
Understanding the interpretation of Total anti-HBc Positive IgM anti-HBc Negative 1 Anti-HBs Negative results is crucial for assessing hepatitis B immunity. These results indicate a past infection, but not current immunity, and may warrant further vaccination or monitoring. By interpreting these tests correctly, individuals can make informed decisions about their health and protect themselves from potential complications.
Komentar